The nexo Retailer protocol defines a set of interfaces between a card payment application and a retail point of sale system. It offers new innovative features such as a clear separation between sale and payment, the provision of a complete series of payment and loyalty services as well as a common approach for all types of architectures and environments.
nexo Retailer Protocol

nexo Retailer Protocol
applications to improve independency
from point of sale and payment solution providers
As the name says, nexo Retailer protocol was developed to address retailer issues and needs. It establishes a clear separation between two software applications that both reside on a point of sale terminal. These are the business application that records a customer sale and a payment application that handles the processing of a card transaction. Both applications need to share cash register peripherals such as printers, displays and card readers.
The sale system
A Merchant uses a sale system to manage the purchase of the goods and services by a customer.
The sale Identifies and registers all the goods and services selected by the customer for the purchase. Prepares the total amount of the purchase, including additional charges and discounts. Makes the payment of the total amount.Performs the delivery of the goods and services to the customer
The payment system
The payment, which is one of the activities of the sale system, is subcontracted to a dedicated payment system when the customer pays with a payment instrument performing electronic payments.
Electronic payment instruments can have various forms depending on the way to transfer payment data and the type of payment instrument.
Examples of a payment instrument are a credit or a debit card, a specific purpose card such as a fleet card, an anonymous stored value card, or a cheque.
A dedicated system performs the payment because of the complexity of the payment process, such as for smart cards, the variety of services attached to the payment, and the security related to electronic payment requiring an isolated and certified product.
The interface between
Sale system & Payment system
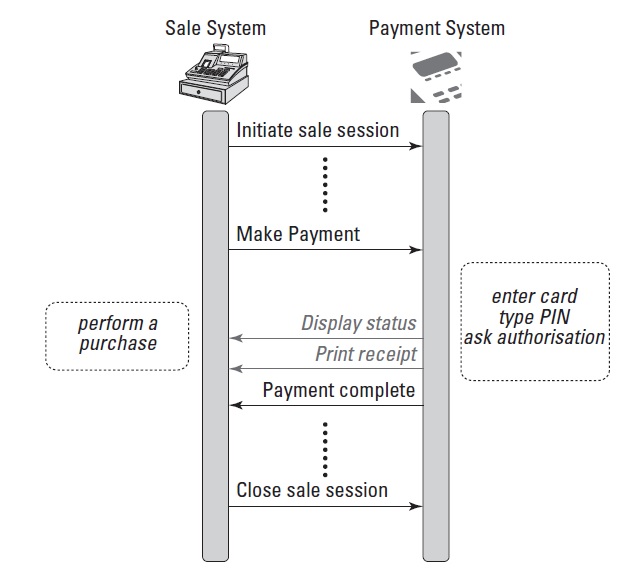
During the payment process, three main services are deployed:
- Cash-back to obtain extra cash along with the goods,
- Cancellation to void a previous payment,
- Refund to reimburse the customer for return of goods,
- Payment reservation for car rental or hotel booking,
- Split payment (if the card authorized), Rebate, tips,
- Dynamic currency conversion (customer chooses his own currency rather than the merchant currency),
- Token, recurring, instalment, aggregation (e.g. small amount).
- loyalty services to credit a loyalty account along with a payment,
- offer discount,
- free items on a purchase,
- redeem a loyalty account.
- Payment / Reversal / Batch / Loyalty / Card Acquisition / Stored Value
- Synchronise the payment system and the sale system,
- Open and close payment services,
- Enable a customer to start the payment before the complete identification of the goods.
- error handling,
- Make a diagnosis on the availability of the payment services,
- Abort a payment that takes too much time,
- Request the result of a previous payment.
- Reconciliation / Get Totals / Balance Inquiry
- Login / Logout / Enable Service / Admin
- Transaction Status / Abort / Event Notification / Diagnosis
- user interface displays information,
- print receipts or other documents,
- requests additional information required for the payment.
- reading a card,
- checking the PIN of a card to authenticate the owner of the card.
- Input / Display / Input Update / Print / Sound / Transmit
- Card Reader APDU / Card Reader Init / Card Reader PowerOff / PIN
NEXO retail protocol
nexo retailer protocol and all the specifications provided would help you undertand several aspects such as:
- The modelisation of the various architectures that could be supported by the protocol.
- The way to use the transport protocol located below the application protocol that is specified.
- The management of the messages, including the dynamic behaviour of the protocol with the error management.
- The specification of the services offered by the protocol, and the specification of how to use these services, by the exchange of sequences of messages.
- The static part of the protocol, definition of the messages and their components.


